
A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system and a Customer Data Platform (CDP) are both used to manage customer data, but differ in their focus. CRM is mainly used to manage customer interactions and communication, while CDP is focused on collecting and unifying customer data from multiple sources to create a comprehensive customer profile. Integrating CRM and CDP can provide a complete picture of the customer journey and behavior.
Customer data is the lifeblood of any business, and it’s essential to manage it effectively.
But have you ever wondered how businesses keep track of all their customer data? It's no secret that managing customer information is critical for building strong relationships and increasing sales, but with so many channels through which customers interact with a business, it can be a daunting task.
That's where customer data management systems come in.
In this blog, we'll explore the difference between two popular systems: CRM and CDP. So, if you're curious about how businesses manage their customer data and how you can improve your own customer relationships, keep reading!
The Basics: What is a CRM and a CDP?
What is a CRM?
A CRM is a tool designed to help businesses manage interactions with customers, including customer data and communication history.
The primary function of a CRM is to improve customer relationships and increase sales by providing insights into customer behavior and preferences.
It provides a centralized database of customer data, enabling businesses to keep track of customer interactions, manage sales pipelines, and analyze data.
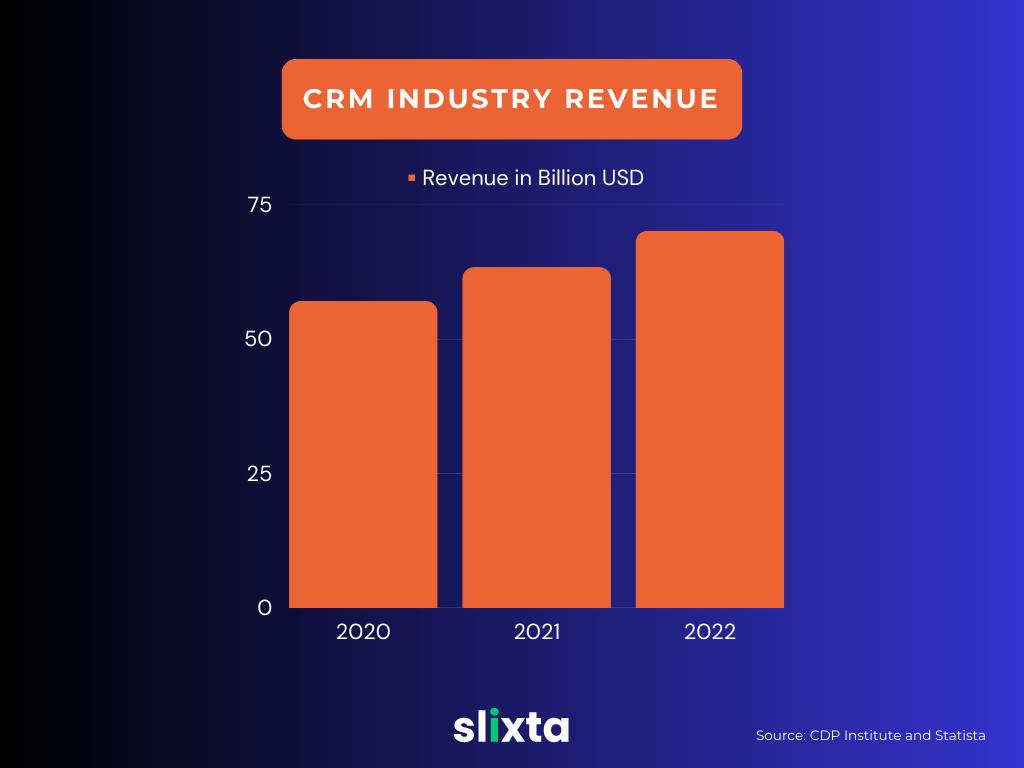
In 2022, the CRM industry generated $70.14 billion in revenue worldwide, a growth from $63.39 billion in 2021, as per Statista.
What is a CDP?
A CDP is a data management system that collects and organizes customer data from various sources, including offline and online interactions.
The primary function of a CDP is to provide a complete, unified view of the customer across all touchpoints.
It aggregates data from multiple sources, such as website analytics, mobile app usage, and online advertising, to create a comprehensive profile of the customer.
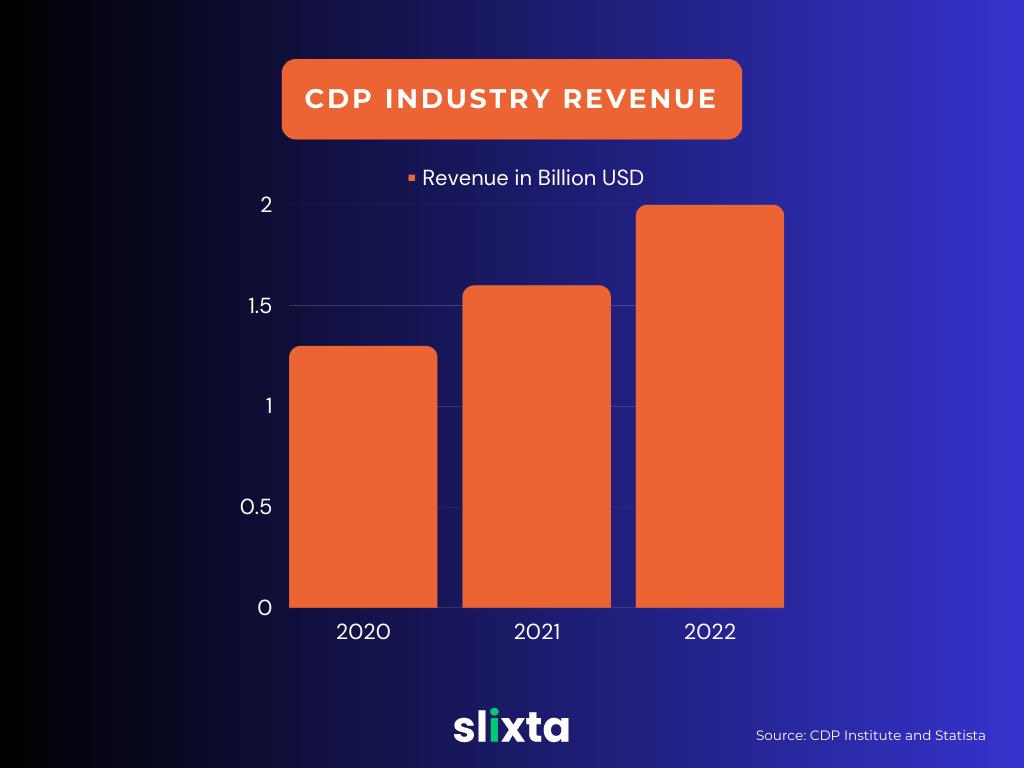
In 2022, the CDP industry generated $2 billion in revenue worldwide, a growth from $1.6 billion in 2021, as per Statista. With CDPs' ability to collect and unify customer data from multiple sources, it has become an integral part of marketing and customer experience management.
Here are some of the key steps involved in how a CDP works:
- Data Collection: The CDP collects data from various sources, such as CRM systems, social media, mobile apps, and websites, and integrates it into a central repository. The data can include customer interactions, behaviors, preferences, and demographics.
- Data Unification: The CDP then unifies the data from different sources into a single, comprehensive view of each customer. This involves matching and merging data points, resolving data conflicts, and enriching the data with additional insights.
- Data Analysis: The CDP uses analytics tools to analyze the customer data and identify patterns and trends. This helps marketers gain insights into customer behavior and preferences, and to create more personalized experiences and targeted marketing campaigns.
- Data Activation: The CDP then activates the customer data by making it available to other marketing technologies, such as email marketing platforms, advertising platforms, and personalization engines. This allows marketers to deliver personalized experiences and targeted campaigns across various channels.
- Data Governance: The CDP ensures that customer data is accurate, compliant with regulations, and secure. This involves implementing data quality controls, privacy policies, and security measures to protect the data from unauthorized access and breaches.

The Evolution of Customer Data Management: From CRM to CDP
Customer data management has come a long way since the days of basic customer relationship management (CRM) systems.
Today, businesses need more than just a tool to store customer information and track interactions. They require a comprehensive system that can collect and manage data from various sources, provide a unified view of the customer, and enable personalized experiences across multiple touchpoints.
That's where customer data platforms (CDPs) come in. A CDP is a software system that collects, integrates, and manages customer data from multiple sources, such as websites, mobile apps, social media, email, and offline interactions.
CDPs use advanced algorithms to process and analyze data, create customer profiles, and provide insights into customer behavior and preferences.
Unlike traditional CRM systems, CDPs are designed to be more flexible and scalable, enabling businesses to manage customer data across all channels and touchpoints. CDPs can integrate with other marketing technologies, such as marketing automation tools, data management platforms (DMPs), and customer experience platforms (CXPs), to deliver seamless customer experiences.
Difference Between CDP and CRM
While both CRMs and CDPs manage customer data, they do so in different ways.
CRMs focus on customer interactions and communications, such as email, phone, and in-person interactions. They rely on user input from sales reps, marketing personnel, and customer service agents to collect data such as customer contact information, purchase history, and communication history. In short, a CRM is a tool for managing relationships.
In contrast, CDPs focus on collecting data from various sources, such as website visits, mobile apps, and offline channels, and use this data to create a complete view of the customer, including their preferences, behavior, and history across all touchpoints. CDPs collect data automatically, without relying on user input, making them more comprehensive and accurate. Here are some of the fundamental differences between CRM and CDP:
- Data Collection: CRM collects data from various sources like social media, email, and website interactions.CDP collects data from multiple sources, including CRM, POS systems, mobile apps, and social media.
- Data Storage: CRM stores customer data in a centralized database that is primarily used by marketing, sales, and customer support teams.CDP stores customer data in a customer profile that can be accessed by any department in an organization.
- Data Usage: CRM is primarily used for marketing and sales purposes, such as lead management and customer segmentation.CDP is used for a wider range of purposes, including personalization, marketing automation, and customer service.
- Data Quality: CRM data is often siloed and incomplete.CDP data is more comprehensive and accurate since it is gathered from multiple sources.
- Real-Time Data: CDP provides real-time customer data, which is crucial for delivering personalized experiences.CRM data is often outdated and lacks real-time insights.
What are the Benefits of Using a CRM vs. a CDP for Customer Data?
Both CRM and CDP platforms offer valuable benefits for managing customer data, but they serve different purposes and have different strengths. Here are some of the benefits of using a CRM vs. a CDP for customer data:
Benefits of using a CRM for customer data:
- Focus on sales and marketing: CRMs are designed primarily for sales and marketing teams, so they offer features like lead tracking, sales pipeline management, and campaign management. These tools can help teams to better target and engage with customers, and ultimately drive more revenue.
- Comprehensive customer profiles: CRMs typically offer a complete view of a customer's interactions with a company, including sales and service history, contact information, and communication preferences. This information can help sales and marketing teams personalize their interactions with customers and improve the customer experience.
- Integration with sales and marketing tools: CRMs often integrate with other sales and marketing tools, such as email marketing platforms, social media management tools, and customer service software. This can help teams to streamline their workflows and make data-driven decisions.
Benefits of using a CDP for customer data:
- Focus on customer experience: CDPs are designed to help companies create a unified view of the customer across all touchpoints and channels. This can help companies to deliver more personalized and relevant experiences to customers.
- Data unification: CDPs are designed to unify customer data from multiple sources, including online and offline interactions.This can help companies to create a more complete and accurate view of the customer, which can lead to better insights and decision-making.
- Scalability: CDPs are designed to handle large amounts of customer data from a variety of sources, making them ideal for companies with complex customer data needs.
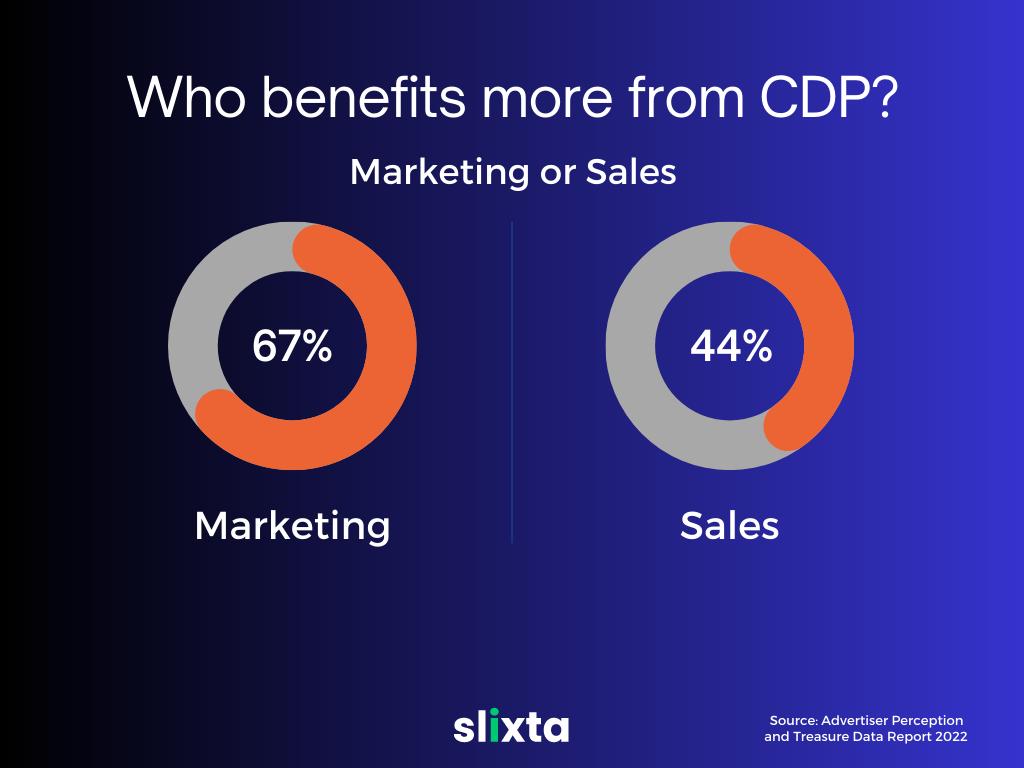
Ultimately, the choice between a CRM and a CDP will depend on the specific needs and goals of your organization. For companies focused on sales and marketing, a CRM may be the best choice. For companies focused on improving the customer experience and unifying customer data from multiple sources, a CDP may be the better option.
Integrating CRM and CDP: How They Can Complement Each Other
While CRMs and CDPs have different functions integrating CRM and CDP can provide businesses with a more complete view of their customers and enable them to deliver more personalized experiences. Here are some ways in which they can complement each other:
- Combining data sources: By integrating CRM and CDP, businesses can bring together their customer data from multiple sources and channels. This can help create a unified view of each customer, including their past interactions, preferences, and behaviors.
- Improved segmentation and targeting: By using the insights gained from both CRM and CDP, businesses can segment their customers more effectively and target them with more relevant and personalized messaging. For example, they can use CRM data to identify customers who have purchased a certain product and combine that with CDP data to understand their other interests and preferences.
- Enhancing customer journeys: By combining the data from CRM and CDP, businesses can create more seamless and personalized customer journeys. For example, a customer who abandons their cart on an e-commerce site could receive an email reminder with product recommendations based on their browsing history and past purchases.
- Better measurement and analytics: By integrating CRM and CDP, businesses can track customer interactions across channels and measure the effectiveness of their marketing and customer engagement efforts. This can help them optimize their campaigns and improve their ROI.
By leveraging the strengths of both systems, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their customers and improve their ability to meet their needs and preferences.
The Future of Customer Data Management: Will CRM and CDP Converge?
The future of customer data management will likely involve a convergence of CRM and CDP technologies. As businesses continue to focus on delivering personalized and seamless customer experiences, they will need a unified platform that can manage all aspects of customer data.
One possibility is that CRM systems will evolve to include more CDP-like features, such as the ability to collect, unify, and activate customer data across multiple channels and touchpoints. This would allow businesses to have a single view of the customer, rather than siloed data in different systems.
Another possibility is that CDPs will expand their functionality to include more CRM-like capabilities, such as sales and marketing automation. This would enable businesses to not only manage customer data but also use it to drive targeted campaigns and generate more revenue.
Ultimately, the convergence of CRM and CDP technologies will depend on customer needs and market demand. As customer expectations continue to evolve, businesses will need to adapt their customer data management strategies to stay competitive.
Conclusion
CRMs and CDPs are both important tools for managing customer data, but they differ in key ways. CRMs focus on managing customer relationships and communication history, while CDPs focus on collecting and unifying customer data across all touchpoints.
By understanding the differences between these two systems and their respective use cases, businesses can make informed decisions about which system to implement and how to integrate them for maximum value. Ultimately, effective customer data management is essential for building stronger customer relationships, increasing sales, and driving business growth.
