
Cross-selling is a sales strategy where businesses promote related or complementary products to customers who are making a purchase. It aims to increase the customer's average transaction value and enhance their shopping experience by suggesting items that align with their interests or needs.
Modern industry standards reveal a striking truth: selling to existing customers boasts a success rate of 60-70%, whereas new customer sales lag behind at a mere 5-20%. This stark contrast emphasizes the pivotal role of cross-selling and upselling in boosting business revenue.
In this blog, we explore the power of Cross-Selling, offering actionable tips to supercharge your revenue through strategic implementation.
What is Cross-Selling?
Cross-selling is a sales and marketing strategy in which a company or business encourages customers to purchase additional or complementary products or services alongside their initial purchase. The goal of cross-selling is to increase the average transaction value and enhance the overall customer experience by suggesting related items that can enhance the utility or value of the primary product the customer is already interested in.
Cross-selling products are sometimes referred to as lateral products. Lateral products are items that are related or complementary to a customer's initial purchase, and they are often suggested during the cross-selling process. The term "lateral" implies that these products are aligned with the customer's interests and needs, enhancing their overall experience with the company.
The goal of cross-selling with lateral products is to provide additional value to the customer while also increasing the company's revenue by selling more than just the main product. Effective cross-selling requires a good understanding of customer preferences, behavior, and buying patterns. This information can be obtained through data analysis, customer segmentation, and tracking customer interactions and purchases.
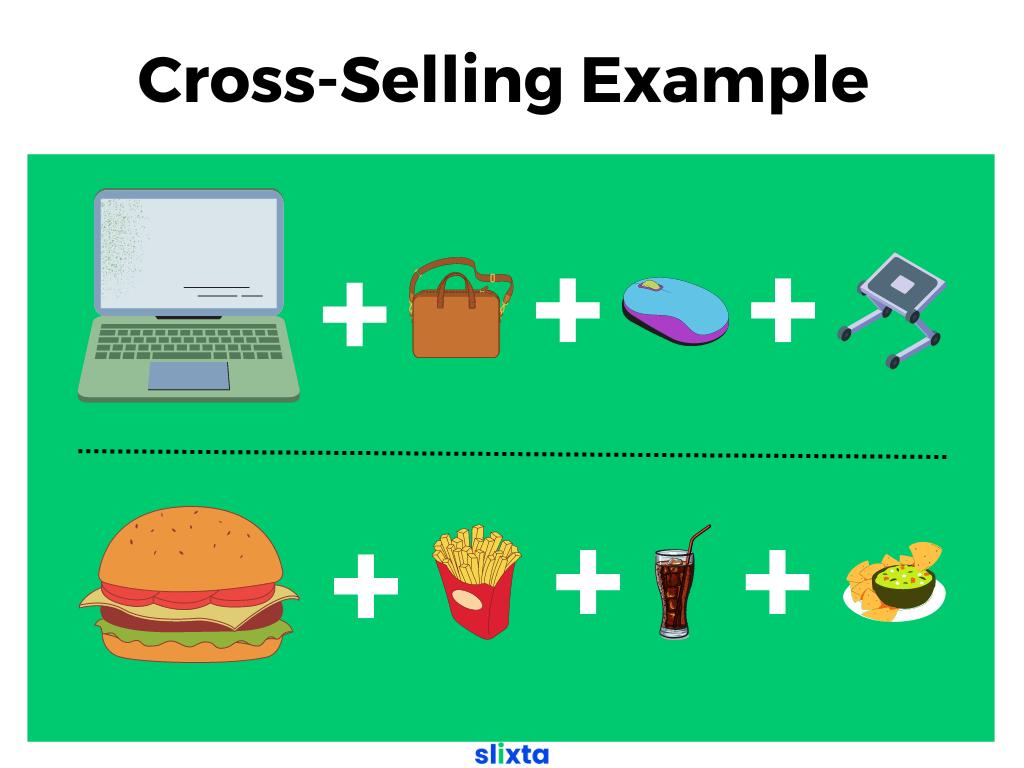
Examples: Cross-Selling
- If a customer is buying a laptop, a cross-selling strategy might involve suggesting accessories such as a laptop bag, a mouse, a laptop stand, or software applications.
- Similarly, in a fast-food restaurant, a cross-selling approach could involve suggesting side dishes, drinks, or desserts to complement the main meal.
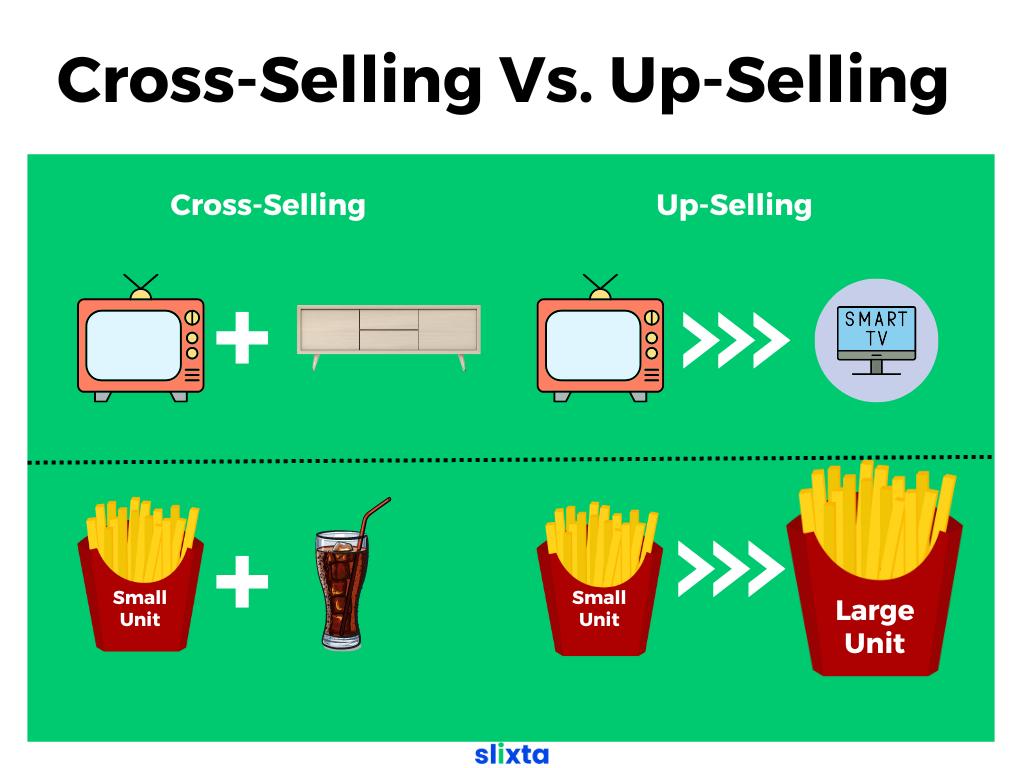
Cross-Selling Vs. Up-Selling
Cross-selling and upselling are both strategies used by businesses to increase their sales and revenue, but they involve different approaches and goals:
Cross-selling
Cross-selling involves suggesting related or complementary products to a customer who is already making a purchase. The additional products offered are lateral or supplementary to the customer's primary choice. The aim is to enhance the customer's experience and provide them with more value by offering items that go well with their initial purchase. Cross-selling typically occurs when the customer is already in the process of buying.
Up-Selling
Up-Selling, on the other hand, involves persuading a customer to upgrade or choose a more premium version of the product they are considering. The goal of upselling is to increase the value of the customer's purchase by encouraging them to spend more on a higher-end or enhanced version of the product. Upselling often happens before the customer finalizes their purchase decision.
Cross-Selling Best Practices
Understand Customer Needs
Before suggesting any cross-sell products, have a deep understanding of your customers' preferences, buying patterns, and needs. Utilize data and analytics to identify potential cross-sell opportunities that align with their interests.
Relevance
The cross-sell items should be relevant and complementary to the customer's primary purchase. Ensure that the suggested products enhance the value or functionality of the main item.
Personalization
Tailor cross-sell suggestions based on individual customer profiles. Use their past purchase history and browsing behavior to provide recommendations that resonate with them.
Timing
Present cross-sell options at the appropriate stage of the customer's journey, ideally when they are considering their primary purchase. Avoid bombarding them with options after the purchase is complete.
Transparency
Clearly communicate the benefits of cross-sell items to the customer. Be honest about how these products can enhance their experience or solve specific problems.
Bundle Deals
Offer bundled packages that combine the main product with related accessories or services at a slightly discounted price. This encourages customers to buy more items together.
Limited Choices
Don't overwhelm customers with too many cross-sell options. Present a limited number of relevant choices to make decision-making easier.
Educate Staff
If you have a sales team, ensure they are well-trained in cross-selling techniques. They should be able to explain the benefits of the suggested products and answer any customer questions.
Customer Consent
Never add cross-sell items to a customer's cart without their explicit consent. Allow them to make the final decision on whether to add these items.
Customer-Centric Approach
Focus on the customer's needs and preferences rather than simply pushing products for the sake of higher sales. Building long-term customer relationships should be a priority.
Post-Purchase Follow-Up
After the customer has made a purchase, consider sending personalized follow-up emails or recommendations based on their recent transaction.
Unethical Cross-Selling Practices
Unethical cross-selling practices involve attempting to increase sales by using deceptive, coercive, or manipulative tactics that exploit customers and compromise their trust. Engaging in unethical cross-selling not only harms customers but also damages the reputation of the business. Here are some examples of unethical cross-selling practices to be aware of:
Misrepresentation: Providing false or misleading information about the benefits, features, or value of a cross-sell product to entice customers into making a purchase.
Hidden Fees
Adding undisclosed fees or charges to cross-sell items, making the final price significantly higher than what the customer was initially shown.
Forced Bundling
Requiring customers to purchase a cross-sell product in order to complete their main purchase, even if they don't need or want the additional item.
Pressure Selling
Using high-pressure sales tactics to manipulate customers into buying cross-sell items they're unsure about or not interested in.
Pre-Checked Boxes
Automatically add cross-sell items to the customer's cart with pre-checked boxes during the checkout process, assuming their consent without explicit agreement.
Non-Transparent Subscription Models
Selling subscription services as cross-sell items without clearly communicating the ongoing costs and terms, leading to unexpected charges.
Ignoring Customer Preferences
Ignoring the customer's expressed preferences or explicitly stated needs and pushing unrelated cross-sell items.
Lack of Information
Failing to provide adequate information about the cross-sell product, preventing customers from making informed decisions.
Taking Advantage of Vulnerable Customers
Identifying vulnerable or less informed customers and using manipulative tactics to persuade them to purchase unnecessary cross-sell items.
Data Privacy Violations
Using customer data obtained without proper consent to target them with cross-selling offers, violates their privacy rights.
Conclusion
Cross-selling isn't just about increasing the bottom line; it's about enhancing the customer experience by offering products that seamlessly align with their needs and desires. As we've explored, the key to successful cross-selling lies in understanding your customers deeply. Through personalized recommendations and carefully timed suggestions, businesses can provide value beyond the initial purchase, fostering long-lasting relationships.
For more valuable insights and information, check out these recommended blogs:
