
Distinguishing First-Party Data from Third-Party Data in Marketing Strategies
Sep 14, 2023
To refine marketing strategies, it's essential to differentiate between first-party and third-party data. First-party data, originating from your own customers, offers reliable, personalized insights. Third-party data, purchased externally, can be less specific. Successful marketing strategies prioritize first-party data to achieve precision and relevance in campaigns.
Two key players in this data-driven arena are first-party and third-party data. First-party data is the information collected directly from your own audience - your loyal customers, website visitors, and subscribers. It's like having an insider's guide to your customers' preferences and behaviors, offering invaluable insights into what makes them tick.
On the flip side, third-party data is like borrowing a neighbor's telescope to peer into your audience's world. It's data collected by external sources and often lacks the intimacy and accuracy of first-party data.
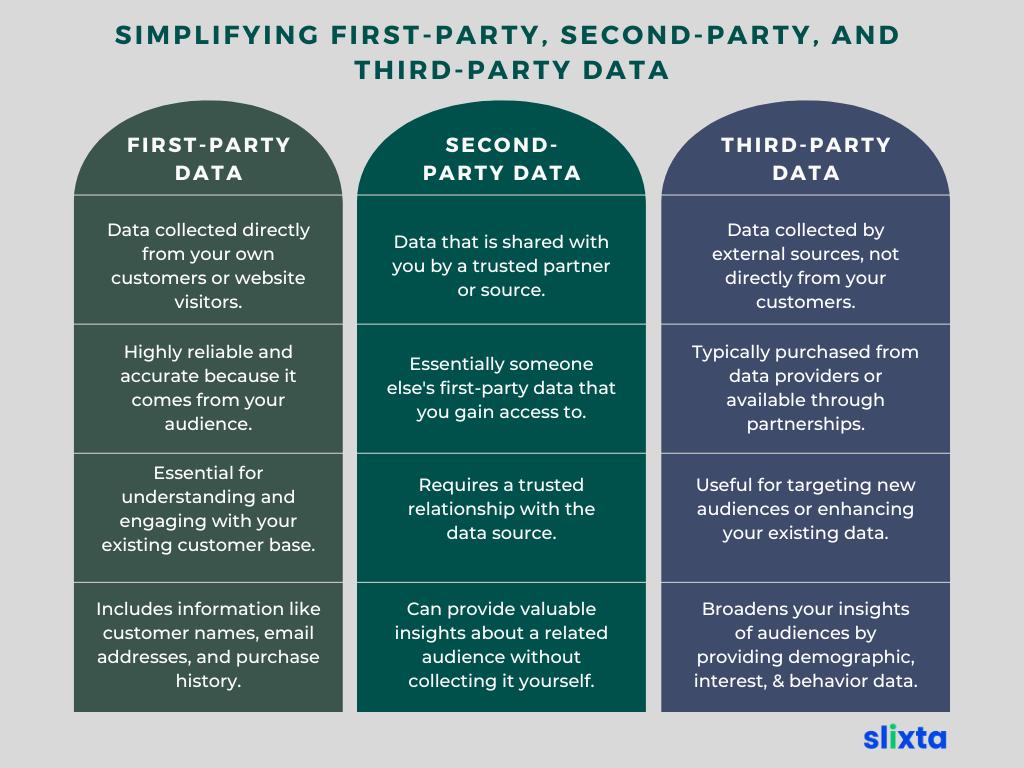
Simplifying First-party, Second-party, and Third-party Data
Let's break down the concepts of first-party, second-party, and third-party data in simple terms
First-Party Data
This is the information you collect directly from your own customers or website visitors. It's like having a conversation with someone and remembering what they tell you. Examples include customer names, email addresses, purchase history, and website behavior on your own platform. First-party data is highly reliable because it comes straight from your audience.
Second-Party Data
Think of second-party data as sharing your friend's notes in school. It's essentially someone else's first-party data that you gain access to through a partnership or arrangement. For example, if a trusted business partner shares their customer data with you, it becomes second-party data for your use. It's often valuable because it's from a source you trust.
Third-Party Data
This is like buying a book on a subject from an expert who has researched and gathered information from various sources. Third-party data is data collected by external sources, not directly from your customers or partners. It often comes from data providers, and it includes a wide range of information about the demographics, interests, and behaviors of people. It can be useful for targeting new audiences or enhancing your existing data.
Distinguishing First-party and Third-party Data in the Context of Marketing Strategies
First-party data and third-party data are two distinct types of data used in marketing strategies. They differ in terms of their source, ownership, and reliability.
Here's a breakdown of the differences between them
Source of Data
- First-Party Data: First-party data is information that a company collects directly from its own customers or audience. This data is generated through interactions with your website, mobile apps, email marketing campaigns, social media profiles, loyalty programs, and other direct touchpoints. It is essentially your own customer or user data.
- Third-Party Data: Third-party data, on the other hand, is data collected by external sources that are not directly affiliated with your business. These sources can include data aggregators, data brokers, publishers, and other companies that sell or share data. Third-party data is typically gathered from various online and offline sources, and it may include demographic, behavioral, and interest-based information about consumers.
Ownership and Control
- First-Party Data: Companies have full ownership and control over their first-party data. They are responsible for collecting, storing, and managing this data, which means they can use it in ways that align with their specific marketing goals and strategies.
- Third-Party Data: Third-party data is owned and controlled by the external sources that collect and provide it. Marketers typically purchase or license this data for their marketing efforts, but they have limited control over its accuracy, quality, or how it's collected.
Reliability and Accuracy
- First-Party Data: First-party data is generally considered more reliable and accurate because it comes directly from your own customers or users. It is based on actual interactions and behaviors, which makes it highly valuable for personalized marketing efforts.
- Third-Party Data: The reliability and accuracy of third-party data can vary widely. Since it's collected by external sources, there is a greater potential for errors, outdated information, or inaccuracies. Marketers often need to assess the quality of third-party data sources before using them.
Use Cases
- First-Party Data: First-party data is often used for personalization, customer segmentation, and retargeting campaigns. It can help businesses better understand their existing customers and improve customer experiences.
- Third-Party Data: Third-party data is typically used for broad audience targeting, prospecting, and market research. Marketers use it to reach new audiences that they may not have direct access to through their own channels.
Crafting Effective Marketing Strategies with Data
The ability to leverage data effectively is the compass that guides your success. To create marketing strategies that resonate with your audience and drive results, you must understand how to wield both first-party and third-party data to your advantage.
First-Party Data: A Personalized Approach
Tailored Messaging: Use first-party data to create personalized marketing messages that speak directly to your customers' preferences and behaviors. Craft email campaigns, product recommendations, and website content that resonate with individual interests.
Customer Segmentation: Segment your customer base based on their purchase history, website behavior, and demographic information. This allows you to target specific groups with tailored promotions and content.
Retention and Loyalty: Use first-party data to nurture existing customer relationships. Send exclusive offers, loyalty rewards, and personalized communications to keep customers engaged and loyal to your brand.
Content Optimization: Analyze website behavior data to optimize your website's user experience. Identify popular pages, improve navigation, and enhance product listings based on customer interactions.
Third-Party Data: Expanding Your Horizons
Market Expansion: Utilize third-party data to identify new market segments and customer demographics that align with your products or services. This data can help you reach untapped audiences and diversify your customer base.
Lookalike Audiences: Create lookalike audiences based on the characteristics of your existing customer base. Third-party data can help you find similar prospects who are more likely to convert.
Competitive Analysis: Leverage third-party data to gain insights into your competitors' customer base and marketing strategies. Identify gaps in the market and opportunities to outperform rivals.
Predictive Analytics: Use intent and behavioral data to predict future customer actions. By understanding consumer intent, you can tailor your marketing efforts to meet their needs before they even express them.
The Power of Data Integration
While first-party and third-party data each offer unique strengths, the real magic happens when you integrate them seamlessly into your marketing strategies.
Here's how to make it happen:
Data Management: Invest in a robust data management platform (DMP) or customer data platform (CDP) to centralize and organize your data from all sources. This enables a holistic view of your customers.
Data Quality: Ensure the accuracy and cleanliness of your data. Regularly clean and update first-party data, and verify the reliability of third-party data sources.
Consent and Privacy: Always prioritize data privacy and obtain consent for data collection and usage. Comply with relevant data protection regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
Analytics and Insights: Employ advanced analytics tools to extract actionable insights from your data. Identify trends, patterns, and opportunities for optimization.
Future of Third-party Cookies
The future of third-party cookies is undergoing a significant transformation driven by evolving privacy concerns and the need to adapt to changing user expectations. One of the most noteworthy developments in this space is Google's decision, as part of its Privacy Sandbox project, to phase out support for third-party cookies in its Chrome browser. This decision has wide-ranging implications for online advertising, digital marketing, and user privacy.
Privacy Sandbox Project Overview:
The Privacy Sandbox is an industry-wide effort to develop new technology that will improve people’s privacy across the Web and apps on Android. The proposed solutions will limit tracking of individuals and provide safer alternatives to existing technology on these platforms while keeping them open and accessible to everyone.
The future of third-party cookies is marked by a shift towards greater user privacy and data protection. Google's Privacy Sandbox project, which includes the phasing out of third-party cookies and the development of alternative technologies, represents a significant step in this direction. Advertisers and marketers will need to adapt and innovate to navigate this evolving landscape while maintaining their ability to deliver effective, privacy-conscious advertising and marketing campaigns.
Conclusion
As we navigate the future of data-driven marketing, it's crucial to adapt to changes in data privacy, such as Google's move away from third-party cookies. Embracing emerging technologies and prioritizing user privacy will be key to success in this dynamic digital world. By understanding and harnessing the power of first-party and third-party data, marketers can continue to connect with the right audiences and drive their marketing strategies toward excellence.
For more valuable insights and information, check out these recommended blogs:
